CCTV News: At 12:12 on May 14, my country used the Long March 2 D carrier rocket at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center to successfully launch the space computing satellite constellation. The satellite successfully entered the predetermined orbit, and the launch mission was a complete success.
The success of this launch mission marks the successful entry of the world's first space computing satellite constellation into orbit.
The success of this launch mission marks the successful entry of the world's first space computing satellite constellation into orbit, and will usher in a new chapter in the global "space computing era".
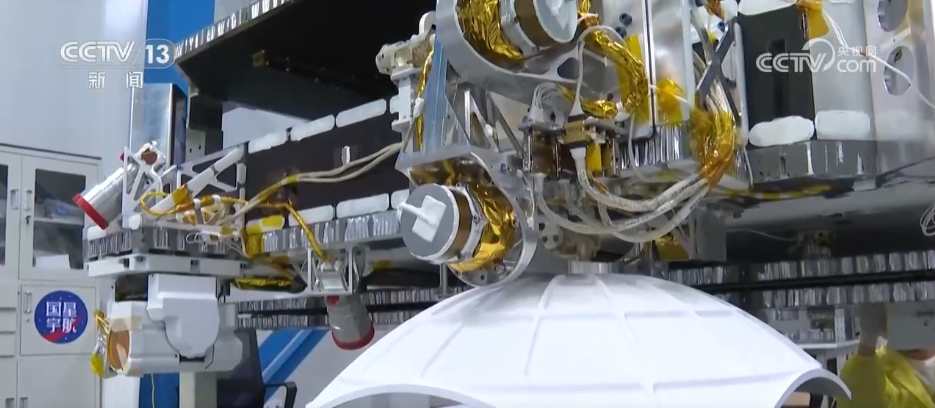
The first 12 constellations computing satellites launched by the "Star Computing" plan adopt the intelligent connected satellite platform developed by Guoxing Aerospace, and are equipped with payloads such as Zhijiang Laboratory's satellite-borne intelligent computers and satellite-borne high-speed routers, realizing "computing power to the sky and in orbit networking". Each satellite is equipped with a satellite-borne intelligent computing system and inter-star communication system, which has space computing and space interconnection capabilities. After the constellations are networked, they will form the world's strongest space computing capabilities.

This constellation builds an open and shared space computing system through inter-star laser high-speed interconnection, stable constellation networking and distributed computing power scheduling to build a space-based intelligent computing infrastructure. On-orbit verification and application of space-based computing basic functions such as building chains, forming networks, and forming clouds in space computing will be completed.
The construction of the "Star Computing" plan will build a future computing power network, realize the transformation from "day count" to "day count" in specific scenarios, meet the growing demand for real-time computing in space, and help my country be the first in the world to build space computing infrastructure, break through the boundaries of the field of artificial intelligence and move from the ground to space.

Create a space-based computing network with 2,800 computing power satellites
This mission achieves the world's first breakthrough in the "zero" space computing constellation. The R&D team said that in the future, it will also build a space-based intelligent computing infrastructure composed of 2,800 computing satellites. What is the significance of developing space computing?
Experts introduced that as the formation of giant constellations has become a global aerospace development trend, the traditional "ground issuance of instructions to satellites-satellite execution-transmitting back to ground" model faces challenges, requiring a large number of independent decision-making and operation systems on the planet, which puts forward new requirements for space computing. Intelligent connected satellites can achieve independent acquisition, analysis and decision-making in orbit, which will greatly improve the quality, efficiency and space of satellite data applications. Zhao Hongjie, executive vice president of Guoxing Aerospace, said that based on powerful space-based computing and interconnection, the cycle of data collection of traditional satellites to information services can be greatly shortened from monthly, weekly or sky-level response time to second level. Through infrared, ads-b and other application payloads, it provides forest fire second level monitoring and perception, and real-time monitoring and positioning of low-altitude vehicles. In terms of scientific exploration, the space computing center can also play the role of a space intelligence center, widely support the real-time on-orbit computing and processing of massive deep space exploration data, and help the calculation requirements of deep space exploration tasks and dynamic optimization of task planning.
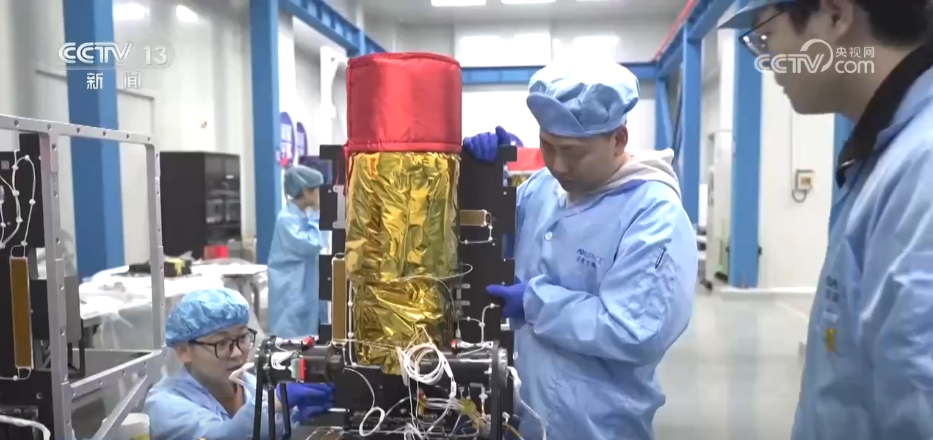

In addition to computing and interconnection capabilities, the first constellation satellite is also equipped with ground remote sensing payloads, as well as a cosmic X-ray polarization detector developed by Guangxi University and the National Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. According to the team leader, they joined hands with the world's first batch of 54 universities, research institutes, enterprises, etc. to launch the "Star Computing" plan to jointly build a space-based intelligent computing infrastructure composed of 2,800 computing satellites. In the future, they will deepen collaborative cooperation with global partners to jointly build an open and shared space computing ecosystem.







